Angelica Chiodoni
Italian Institute of Technology, Italy
Title: Nanostructured MnxOy as catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction
Biography
Biography: Angelica Chiodoni
Abstract
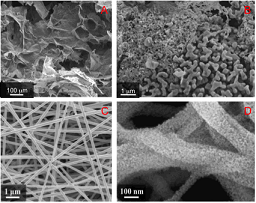
In the framework of the growing concerns about global warming, the development of new and clean energy resources represents one of the major scientific challenges. In particular, in fuel cells and metal-air batteries, the electrochemical Oxygen Reduction Reaction (ORR) occurring at the cathode is one of the key limits for their further development and requires electrocatalysts to increase the reaction efficiency. Manganese oxides are among the most considered non-precious metal-based catalysts due to their low cost, relatively high abundance, low environmental impact and considerable electrocatalytic activity. In this work we present nanostructured manganese oxides in the form of xerogels (obtained by means of the sol-gel plus freeze- drying techniques) and in the form of nanofibers (obtained by means of the electrospinning technique) as catalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction. They were synthesized by employing manganese acetate as the Mn source and by employing environmental friendly (water is the used solvent) templating agents, such as agar and polyethylene oxide, for xerogels and nanofibers respectively. To investigate the oxidation process forming the manganese oxides species, structural and morphological characterizations as in-situ X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were performed on both the nanostructures. The obtained materials were composed by Mn3O4, Mn2O3, or a mix of both, depending on the calcination temperature. The catalytic performance of the two nanostructured catalysts were characterized by means of the rotating ring disk electrode technique by using 4-electrodes measurements. Both xerogels and nanofibers showed good performances for the oxygen reduction reaction, with n values between 3.5 and 3.7, meaning a predominant 4-electrons reduction pathway.