Cedric Loubat
Specific Polymers, France
Title: Specific Polymers – Alkoxysilane and phosphonic acid functional groups to improve compatibility between inorganic surfaces and polymers
Biography
Biography: Cedric Loubat
Abstract
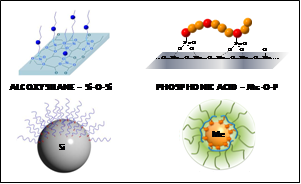
Specific Polymers (2003, Castries, France) is a SME with 12 employees acting as R&D service provider and scale up producer in the field of functional monomers and polymers with high specificity. Through its activities, Specific Polymers is involved in scientific research in various application fields like aeronautic, building industry, biomedical area, automotive, green materials or optoelectronic. Even if the research activity of the company mainly focuses on organic polymers based materials, the problems of interaction between organic and inorganic matters have been the subject of numerous studies. Indeed, in most of the cases, the chemical nature of interaction between the inorganic particles and the polymer drives the performance of the resulting system. In this field, Specific Polymers researches are mainly oriented toward (macro) molecules bearing either alkoxysilanes or phosphonated groups. On one hand, polymers bearing alkoxysilane groups are of a great interest for inorganic material surface modification, preparation of functional nanoparticles, or synthesis of sol-gel based hybrid materials. Indeed, the hydroxyl groups located on the inorganic surfaces can react with the alkoxysilanes moieties of functional polymers conducting to hybrid or composite materials exhibiting outstanding properties. On the other hand, phosphonated groups have the ability to bind metal or metal oxides (iron, aluminium, cerium, titanium, uranium, ITO, gadolinium, nickel, copper, zinc, calcium, quantum dots, nano-metals, etc.) and thus can also be used for functionalization of surfaces or particles. As for example, phosphonic acid functionality was often found to be superior to alkoxysilanes moieties for binding inorganic substrates other than silica, because of the higher robustness and stability of metal-OP over metal-OSi bonds. The interest of both alkoxysilane and phosphonated moieties for surface metal or glass surface modifications,1 functionalization of (nano)particles,2,3 compatibilization of inorganic components into polymeric matrix or functional hybrid sol-gel materials in very versatile applications is highlighted.