
Golibjon R. Berdiyorov
Hamad bin Khalifa University, Qatar
Title: First-principles study of optoelectronic, transport and ionic sieving properties of Ti3C2X2 (X=O, OH and F) Mxene
Biography
Biography: Golibjon R. Berdiyorov
Abstract
MXenes, a new family of low-dimensional materials, have received a lot of interest due to their unique physical, chemical, and mechanical properties [1]. MXenes have already shown a great potential in storage applications due to their impressive capacitive performance [2]. Here, we study the electronic and transport properties of Ti3C2 MXene using density-functional theory (DFT) in combination with the nonequilibrium Green’s function formalism [3, 4]. Fluorinated, oxidized and hydroxylated surfaces are considered. We found that the surface termination has a considerable impact on the electronic transport [3]. For example, the fluorinated sample shows the largest transmission, whereas surface oxidation results in considerable reduction of the electronic transmission. Such enhanced transmission originates from the extended electronic states and smaller variations of the electrostatic potential proï¬le. We also study the effect of lithium and sodium ion adsorption on the electronic transport properties of the MXene [4]. Optical properties of MXene are also affected bysurface functionalization [5]. For example, in the visible range of the spectrum, the oxidized sample shows larger absorption, whereas surface fluorination results in weaker absorption as compared to pristine MXene.
Recently, MXene nanosheets have also emerged as ultrathin and high-flux sieving membranes [6]. In addition to ultrafast water flux, both hydration radius and charge dependent transport of ions have been observed. MXenes are also shown to be highly resistive to biofouling [7]. Here we present the results of our DFT calculations to explore the possible mechanisms for the charge-selective ionic transport through Ti3C2X2 (X=O, OH or F) Mxene [8, 9]. We show that the charge selectivity originates from the charged nature of the MXene layers: the system shows dynamic response to the intercalating ions, even in their hydrated states, by changing the interlayer spacing. We also address the stability of MXene membranes and discuss the possibilities of enhancing their stability by molecular and nanoparticle intercalations. We present the results of our atomistic scale calculations for structural, electronic water sieving properties of hydrophobic graphene and hydrophilic MXene monolayers (see Fig. 1).
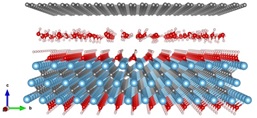
Fig 1. Atomistic structure of graphene (top) and Ti3C2(OH)2 MXene (bottom) bilayer with intercalating water molecules.
Recent Publications
1. M. Naguib, V. N. Mochalin, M. W. Barsoum, Y. Gogotsi, 25th Anniversary Article: MXenes: A New Family of Two-Dimensional Materials, Adv. Mater. 26, 992 (2014).
2. J.-C. Lei, X. Zhang, Z. Zhou, Recent advances in MXene: Preparation, properties, and applications, Front. Phys. 10, 276 (2015).
3. G. R. Berdiyorov, Effect of surface functionalization on the electronic transport properties of Ti3C2 MXene, Europhys. Lett. 111, 67002 (2015).
4. G. R. Berdiyorov, Effect of lithium and sodium adsorption on the electronic transport properties of Ti3C2 MXene, Appl. Sur. Scie. 359, 153 (2015).
5. G. R. Berdiyorov, Optical properties of functionalized Ti3C2T2 (T = F, O, OH) MXene: First-principles calculations, AIP Advances 6, 055105 (2016).
6. C. E. Ren, K. B. Hatzell, M. Alhabeb, Z. Ling, K. A. Mahmoud, Yury Gogotsi, Charge- and Size-Selective Ion Sieving Through Ti3C2 T x MXene Membranes, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6 (2015) 4026-4031.
7. K. Rasool, K. A. Mahmoud, D. J. Johnson, M. Helal, G. R. Berdiyorov, and Y. Gogotsi, Efficient Antibacterial Membrane based on Two-Dimensional Ti3C2Tx (MXene) Nanosheets, Scientific Reports 7, 1598 (2017).
8. G. R. Berdiyorov, M. E. Madjet, and K. A. Mahmoud, Ionic transport through Ti3C2(OH)2 MXene: ï¬rst principles calculations, Applied Physics Letters 108,113110 (2016).
9. G. R. Berdiyorov and K. A. Mahmoud, Effect of surface termination on ion intercalation selectivity of bilayer Ti3C2T2 (T=F, O and OH) Mxene, Applied Surface Sciences 416, 725-730 (2017).

