
Henri Jaffrès
Unité Mixte de Physique, France
Title: Spinorbitronics at Interfaces for THz Emission
Biography
Biography: Henri Jaffrès
Abstract
Spin-Hall Effects at short lengthscale in bulk heavy metals like Pt or W [1] and spin-orbit related phenomena like Inverse-Edelstein Effect [2-3] at interfaces are presently at the basis of new spintronics functionalities. Combined with RF-spin-pumping Ferromagnetic Resonance (FMR) pumping, spin-orbit give rise to AC and DC spin-to-charge current conversion. Those combined techniques enable to probe the interface quality and physical properties. In the same way, in an extented description out-of FMR resonance, it was recently reported that THz emission of relatively high power may be realized in the same kind of heterostructures composed of ferromagnetic (FM) and non-FM metal films via dynamical spin-to charge conversion and time- dependent spectroscopy (TDS) [4-6].
In that mind, we will present our last results of THz emission provided by optimized growth bilayers composed of a high-spin orbit material in contact with a ferromagnetic layerCo/Pt, NiFe/Au:W). Those bilayers state-to-the art model systems in experiments combining RF-spin pumping and spin-to-charge conversion by ISHE [7-8]. Here, experiments consist in exciting magnetization and spin-currents within the FM layer via femtosecond laser excitation and measuring, in the picosecond timescale, the relaxation of the correlated spin and charge currents responsible for THz dipolar emission. The THz emission provided by these spintronics bilayers reaches the power of ZnTe semiconductor technology. We will display the first THz emission results obatined on a-Sn/InSb topological insulators.
Moreover, in order to study the SHE spin-current profiles and address their properties in those [Co,Ni]N/Pt and [Co,Ni]N/Au:W multilayers, we have analyzed their Anomalous Hall effect (AHE) signals showing up a characteristic AHE spin-inversion from Pt to Au:W samples. We analyze our results in the series of samples: the exact conductivity profile across the multilayers via the 'extended' Camley-Barnas approach [9] and the spin current profile generated by spin-Hall effect. We will discuss the role of the generalized spin-mixing conductance on the spin-transport properties and spin-orbit torques.
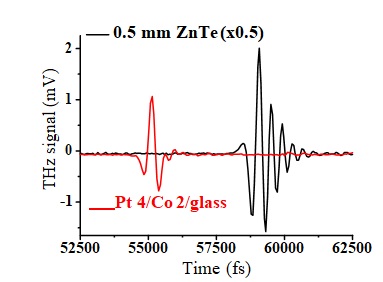
Figure 1 | Time-Domain-Spectroscopy (TDS) THz signals of Pt(4nm)/Co(2nm)/Quartz bilayer systems obtained by femtosecond (100 fs) laser excitation (400 mW). The fs laser exciation causes magnetization precession associated to a spin-current (spin displacement). This is transformed afterward to a lateral charge current responsible for dipole oscillations and THz emission. The signal is compared to a reference ZnTe characteristic THz emission (amplitude x 0.5).
Recent Publications
1. J. Sinova, S. O. Valenzuela, J. Wunderlich, C. H. Back, and T. Jungwirth, Rev.Mod. Phys. 87, 1213
2. J. C. Rojas Sánchez, L. Vila, G. Desfonds, S. Gambarelli et al., Nat. Comm. 4, 2944 (2013)
3. J.-C. Rojas-Sánchez, S. Oyarzún, Y. Fu, A. Marty et al., Phys. Rev.Lett. 116, 096602 (2016)
4. T.J. Huisman et al, Nat. Nano., DOI 10.1038 (Nnano2015) 331 (2015).
5. T.Seifert, and All Efficient metallic spintronic emitters of ultrabroadband terahertz radiation Nature photonics 10:483488, (2016).
6. D. Yang et al.. ‘Powerful and tunable thz emmiters based on the Fe/Pt magnetic heterostructure’, Adv. Opt. Mat.(2016).
7. J. C Rojas Sanchez et al., Phys Rev Lett. 112, 106602 (2014).
8. P. Laczowski et al., Applied Physics Letters 104 (14), 142403, 2014. 28 (2014). P. Laczowski et al., Phys. Rev. B 92, 214405 (2015)
9. R. E. Camley, J. Barnas, Phys. Rev. Lett. 63, 664 (1989); J. Barnas, A. Fuss, R. E. Camley, P. Grünberg, and W. Zinn, Phys. Rev. B 42, 8110 (1990)

