Yu-Chen Fa
National Sun Yat-sen University, Taiwan
Title: MSE-11: Chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles modified with folate use for doxorubicin released
Biography
Biography: Yu-Chen Fa
Abstract
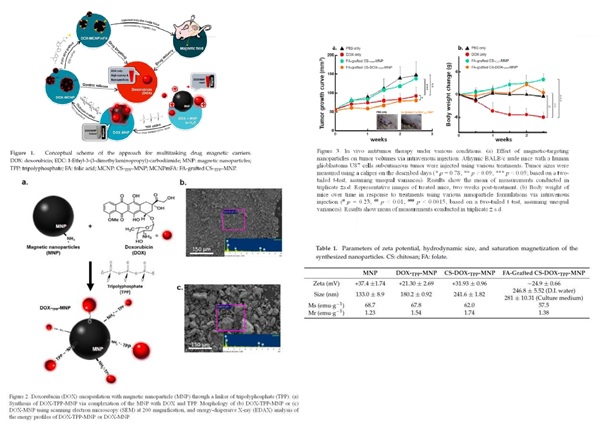
In clinical tumor therapy, chemotherapeutic routes have caused severe side effects; current delivery methods are unsatisfactory. Successful design of a remotely folate (FA)-grafted chitosan (CS)-coated magnetic nanoparticle (MNP) with low toxicity, has been achieved (Figure 1). A chemotherapeutic drug such as doxorubicin (DOX), is loaded in the MNP-based matrix (FA-grafted CS-DOX-TPP-MNP), which is coated by an activated target tumor molecule of FA-grafted CS biopolymer with the inclusion of tripolyphosphate (TPP) as a linker (Figure 2). The resultant nanocomplexes exhibited random aggregates (~240 nm) and zeta potential (− 24.9 mV) (Table 1). In vivo experiments using athymic BALB/c nude mice with human glioblastoma U87 cells in a subcutaneous tumor model revealed that magnetic guidance of FA-grafted CS-DOX-TPP-MNP, injected via the tail vein, significantly decreased tumor growth (Figure 3). This manuscript demonstrates the feasibility of magnetizing control of FA-grafted CS-DOX-TPP-MNP to enhance the localization of drug release.